What is Environmental Health?
This field involves the science and practice of preventing human injury and illness and promoting well-being. Environmental Health professionals work to identify and evaluate environmental sources and hazardous agents and work to limit exposure to hazardous physical, chemical, and biological agents in the air, water, soil, food safety, and other areas that may harm human health. The environmental health officer provides advice to other agencies that also protect public health.
Our health and wellbeing are influenced both directly and indirectly by the environment around us. Environmental health focuses on how our surroundings affect our physical and mental health. To maintain good health, we need environments that are safe, clean, and supportive. The conditions in which we live play a significant role in shaping our overall wellbeing. We rely on the environment for essential resources that sustain life, including:
- fresh air
- clean and safe drinking water
- healthy food
- secure and livable housing

Our Roles
Environmental health officers have several roles requiring enforcement, promotion and advocacy attributes that they may play to mitigate health risks and avoid health and safety hazards that include risk of infectious diseases are:
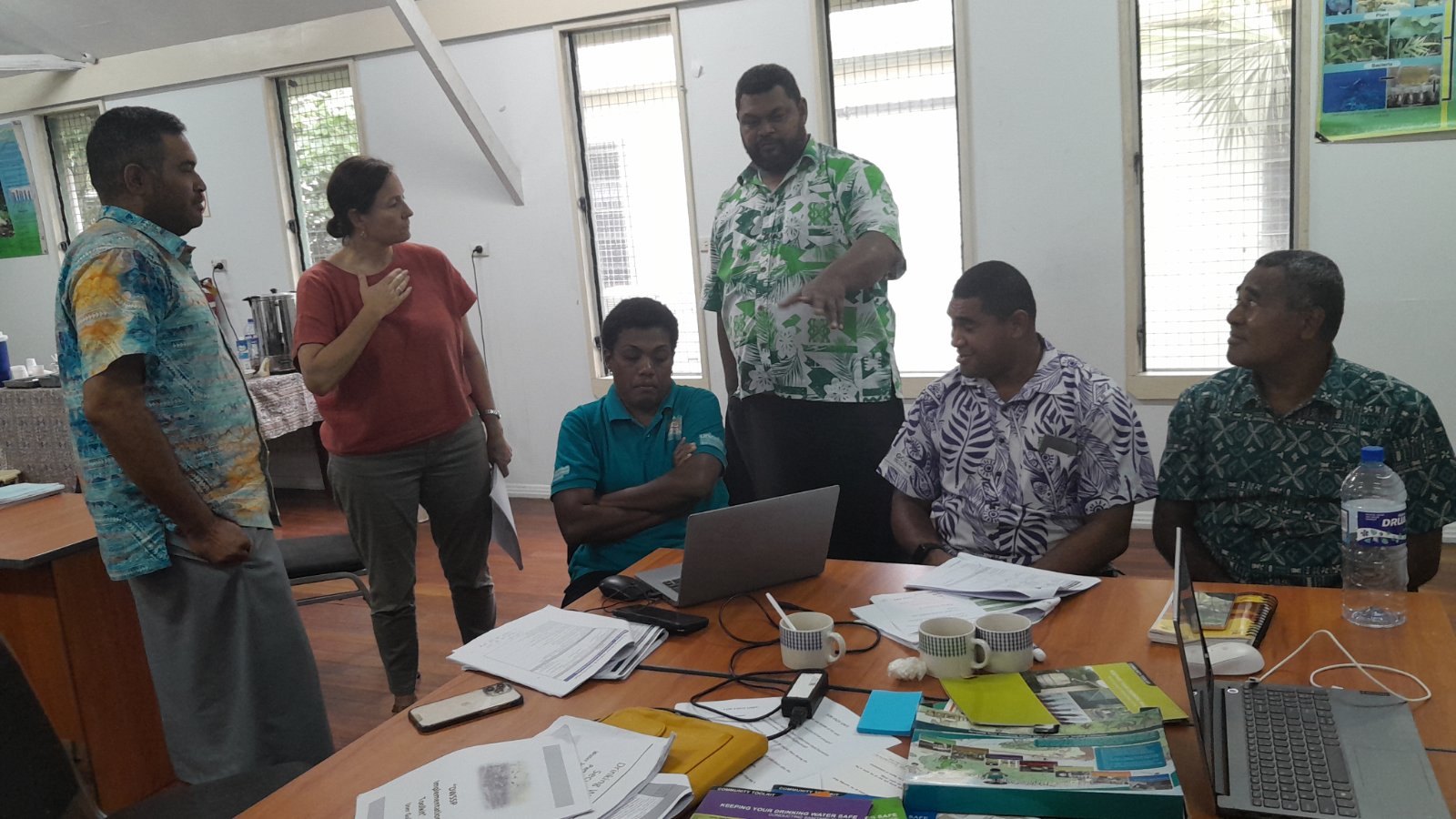
Safety Inspections
A large portion of what an environmental health officer does is spent on routine inspections of various environments to make sure they are safe. They often spend time inspecting businesses of all types, including small and large manufacturers for all kinds of environmental situations including pest infestation, noise complaints, toxic contamination, air pollution, and investigating complaints. In this case, environment includes any space in which humans and animals might exist. This includes buildings of every variety, bridges, parks and other outdoor spaces, and large compounds such as school campuses and amusement parks. Some environmental health officers are contracted with specific companies in the private sector and work exclusively on their spaces. Other health officers work for the government. Still others do freelance work at a wide variety of sites. These inspections can include food premises for food safety to protect people from food poisoning, occupational health situations, pest control, and pollution control, among other things, to promote hygiene standards. Public health inspectors often need good communication skills for writing reports to communicate with local authorities in promoting health and
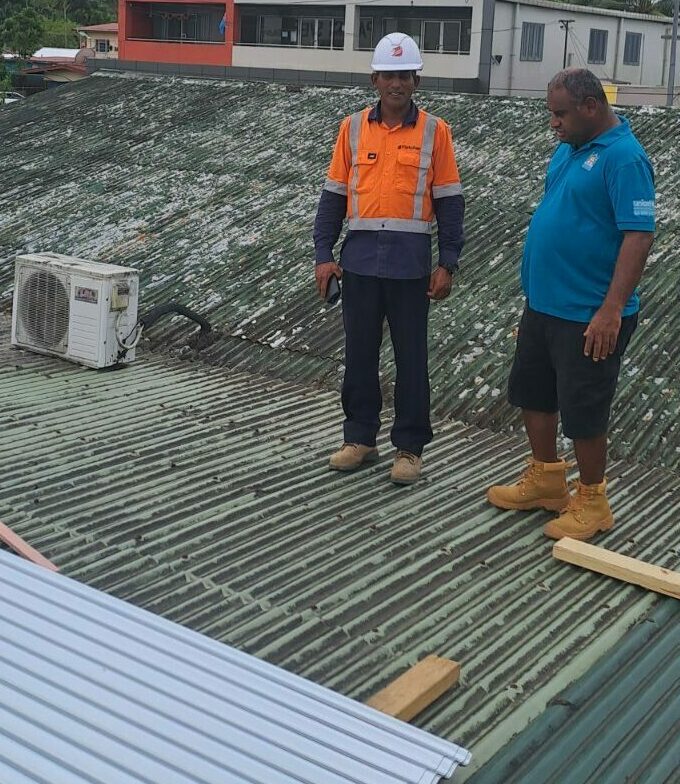


Identification of Hazards
During their safety inspections, environmental health officers are responsible for overseeing removal of all potential safety hazards. These include all biological, chemical, and radiological materials that could violate national and industry-specific regulations. Officers submit samples of suspect materials for professional analysis and then make final decisions about their potential threat and how to proceed. Their professional practice often involves wearing protective clothing and providing essential advice to local authority regarding health hazards. The environmental health officer works to eliminate the risk of environmental pollution such as air pollution, food poisoning, and issues that may lead to public health emergencies.
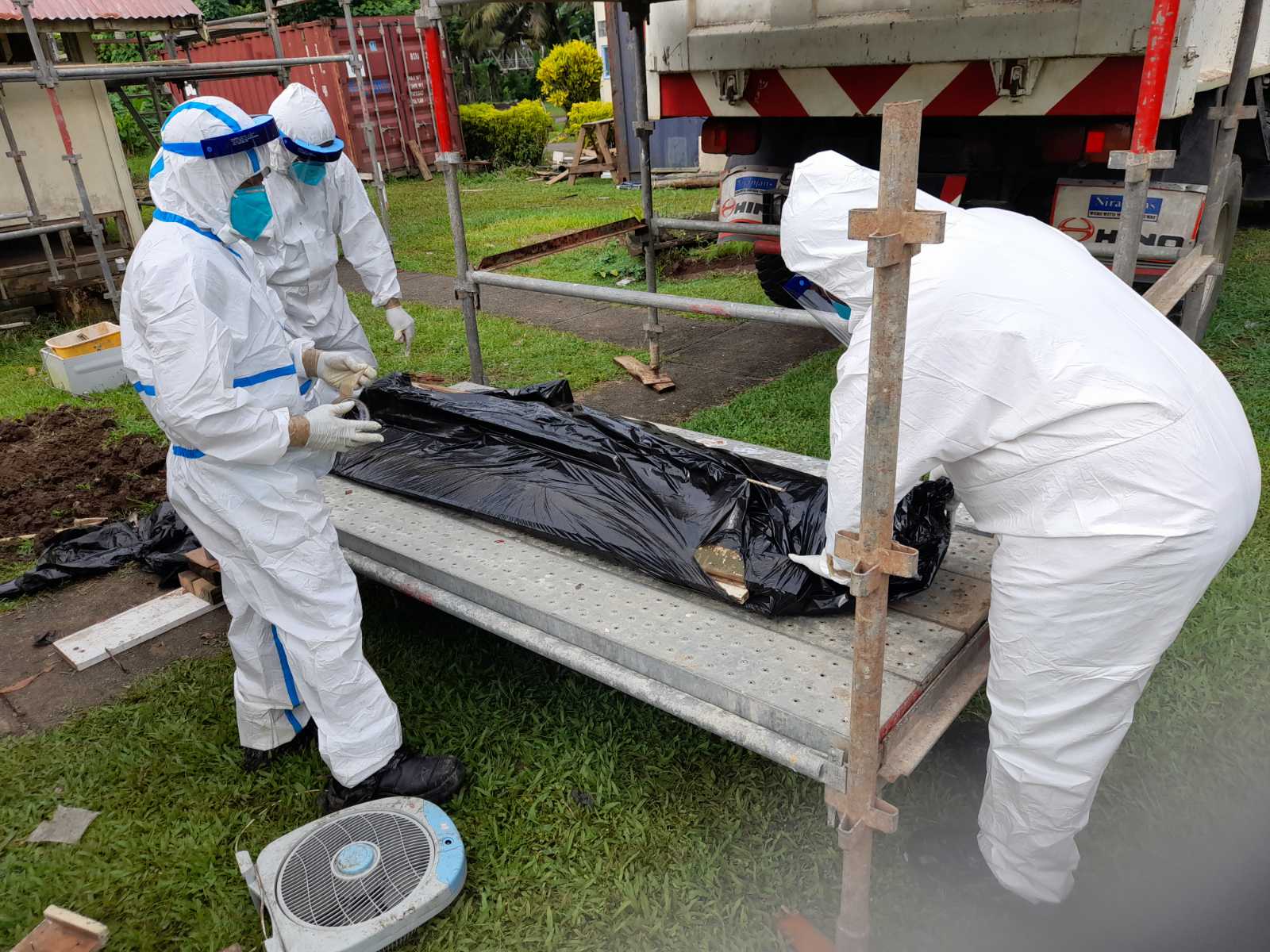
Removal of Hazards
When suspect materials are found to pose risks to public health, the environmental health officer is responsible for ensuring that all traces are removed from the premises. Since environmental hazards cannot simply be tossed out with the day’s trash, this involves locating and coordinating with the proper hazardous waste removal agencies. The environmental health officer must then identify the original source of the hazardous material to determine if a one-time removal is sufficient or if the situation calls for a more systemic solution to promote health and safety. These hazards may include food safety, pest control, and infectious diseases. In signing off on the final inspection, the health officer effectively communicates with local authorities that he or she feels fully confident that the premises are safe for human occupation.


Training
These health officers conduct periodic training courses to help all occupants remain safe and healthy. They design and implement training programs, procedures for preventing illness and injury, and protocol for how to handle health and safety threats, including infectious diseases and food safety issues that arise. Health officers are responsible for ensuring that these trainings are carried out often enough to ensure that all occupants are up to date on the policies and procedures, and trainings are often concurrent with updated inspections.
Emergency Management
Even the most thorough inspections and intensive trainings cannot prevent all accidents and emergencies. Many environmental health officers are responsible for overseeing actions in response to such events. These can range from minor accidents involving one or a few people to large scale disasters. Health officers must be prepared for the full spectrum of emergencies, including those caused by both human error and nature.


